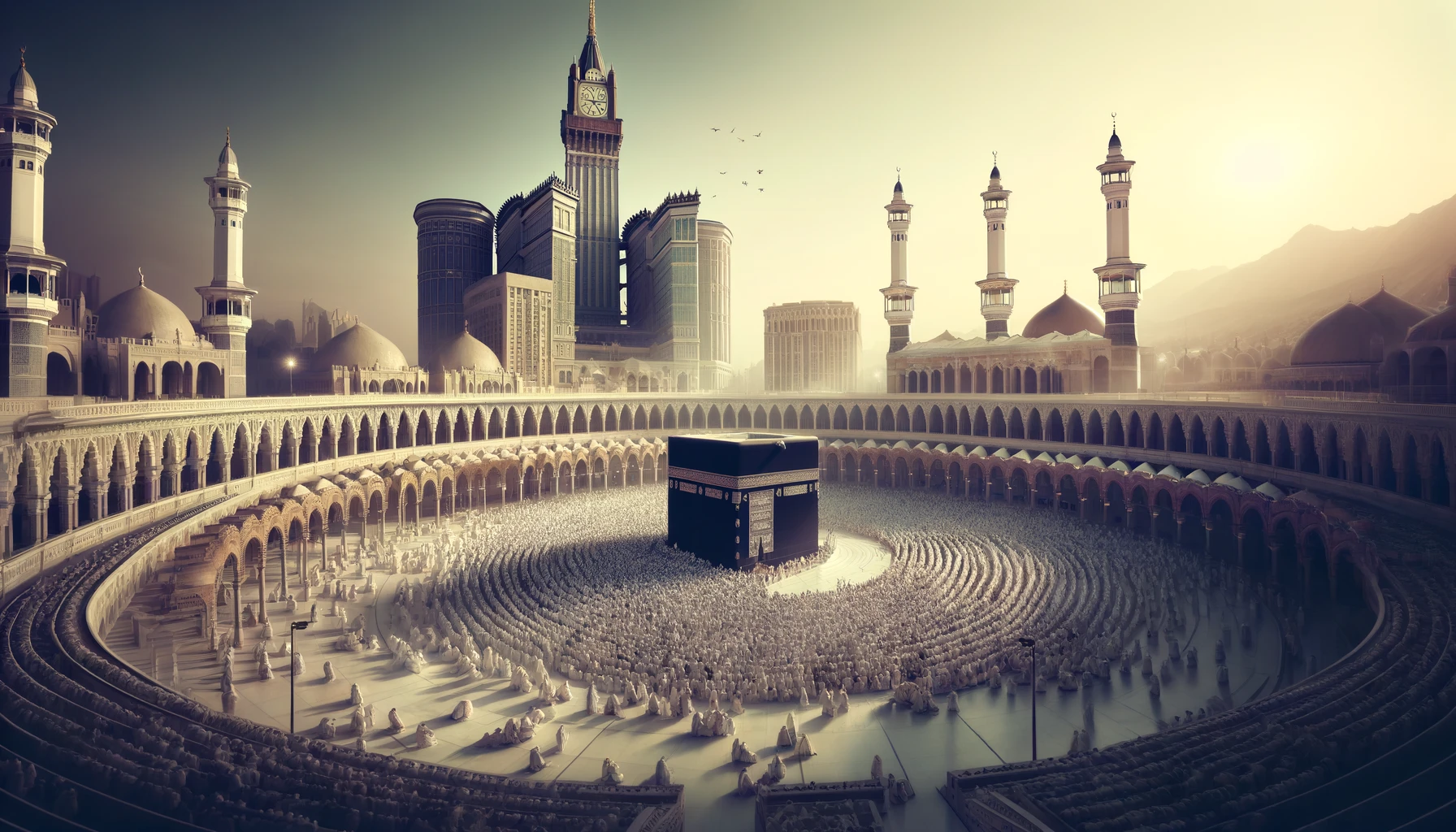
Makkah, the heart of Islam, holds a profound place in the lives of Muslims worldwide. Revered as the birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) and home to the sacred Kaaba, it symbolizes unity, faith, and devotion. Muslims face Makkah in daily prayers, and millions journey there annually for Hajj and Umrah. The city’s spiritual atmosphere, steeped in history, connects believers deeply to their faith, promoting peace, humility, and submission to Allah. Here, we explore Makkah’s historical importance, its role in Islam, and why it stands as a pinnacle of faith for Muslims.
Introduction
The Importance of Makkah in Islam cannot be overstated. Known as the holiest city in the Islamic faith, Makkah is the birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) and the site of the Kaaba, the sacred structure Muslims around the world face during prayer. Beyond its historical significance, Makkah holds a central role in Islamic spirituality, culture, and unity, drawing millions of pilgrims each year for Hajj and Umrah. This article explores why Makkah is revered in Islam, the significance of its sacred sites, and its role in unifying Muslims globally.

Historical Background: Importance of Makkah in Islam
The importance of Makkah in Islam begins with its ancient roots. Located in the Arabian Peninsula, Makkah was a crucial trading hub long before the advent of Islam, connecting caravans from Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Its historical and economic relevance was deepened by its religious significance as the home of the Kaaba, a site associated with Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) and his son Ismail (Ishmael), whom Muslims revere as forefathers of monotheism.
According to Islamic tradition, Allah commanded Ibrahim and Ismail to build the Kaaba as a house of worship dedicated to the One God. This structure became a focal point of spirituality for early monotheists and, eventually, for Muslims worldwide. The Kaaba’s establishment marked Makkah as a place of divine connection, linking followers of Islam with the prophets of the past.
The Role of the Kaaba and Its Importance in Islam
The importance of Makkah in Islam is highlighted through the Kaaba, often called the “House of Allah.” It is toward the Kaaba that Muslims turn in prayer, reinforcing the city’s unifying role in Islam. Muslims believe that the Kaaba was initially built by Ibrahim and Ismail and later became central to the Islamic faith during the Prophet Muhammad’s time.
Qibla – The Direction of Prayer
The Kaaba’s importance is underscored by its role as the Qibla (direction of prayer). Muslims worldwide, from Africa to Asia, turn toward Makkah during their five daily prayers. This universal orientation symbolizes unity, aligning the hearts of over a billion Muslims toward a single spiritual center.
Quranic Significance of the Kaaba
The Kaaba and Makkah are repeatedly mentioned in the Quran. One prominent verse reads:
“Indeed, the first House [of worship] established for mankind was that at Makkah – blessed and a guidance for the worlds.” (Quran 3:96)
Such verses emphasize Makkah’s role as a guiding force and blessed place in Islam, connecting Muslims with a divine heritage.
Hajj and Umrah: Pilgrimage and the Importance of Makkah in Islam
Among the Five Pillars of Islam, Hajj – the pilgrimage to Makkah – is one of the most sacred obligations for Muslims. Every year, millions of Muslims gather in Makkah for Hajj, seeking spiritual renewal and forgiveness.
Significance of Hajj in Islam
Hajj is performed once a year and involves several rituals that hold deep meanings. For example, the act of Tawaf, or circumambulating the Kaaba, represents Muslims’ dedication to Allah. The Sa’i between the hills of Safa and Marwah recalls the story of Hagar (Hajar), who ran between these hills searching for water for her son Ismail. Hajj culminates on the plains of Mount Arafat, where pilgrims stand in prayer, symbolizing the Day of Judgment.
Umrah: A Year-Round Pilgrimage
While Hajj is performed annually during a specific month, Umrah can be undertaken at any time of the year. Though not obligatory, Umrah is a sacred act of worship that draws millions to Makkah year-round. Both Hajj and Umrah highlight the importance of Makkah in Islam as places where Muslims cleanse their souls and renew their connection with Allah.

Sacred Sites and Their Importance in Makkah
Beyond the Kaaba, the city is home to other revered landmarks that contribute to the importance of Makkah in Islam. These sites carry historical and spiritual significance, deepening the city’s meaning for Muslims.
Masjid al-Haram (The Sacred Mosque)
Surrounding the Kaaba, Masjid al-Haram is the largest mosque in the world. Known as the Sacred Mosque, it is a place of tranquility and worship. Pilgrims performing Hajj and Umrah gather here, creating a powerful image of Muslim unity and devotion. The mosque is constantly being expanded to accommodate the growing number of pilgrims, emphasizing its centrality to the Muslim world.
Zamzam Well
Another critical site in Makkah is the Well of Zamzam, which is believed to have sprung miraculously for Hagar and her son Ismail. According to Islamic tradition, the well’s water is blessed, and many Muslims seek to drink from it during their pilgrimage. This sacred water is seen as a reminder of Allah’s mercy and provision, further elevating the importance of Makkah in Islam.
Mount Arafat and Mina
During Hajj, Muslims visit Mount Arafat, where Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) delivered his final sermon, emphasizing justice, equality, and the core principles of Islam. The plains of Mina are also significant, as they represent the location of the symbolic stoning of the devil, reminding Muslims of the constant struggle against evil.
Why Makkah is Important to Islam
The importance of Makkah in Islam extends beyond its historical sites and rituals. Makkah is a powerful symbol of unity, with Muslims from all races, languages, and cultures gathering for worship. This shared destination demonstrates the equality and brotherhood that Islam promotes, as pilgrims dress in simple white garments that remove social distinctions.
Moreover, Makkah, as the birthplace of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH), holds a special place in Islamic heritage. It was here that he began his prophetic mission, spreading the message of Islam and establishing Makkah as the heart of the faith.

Global Impact of Makkah: A Center for Unity and Peace
Makkah’s significance is felt not only by those who visit but also globally. Millions of Muslims face Makkah in their prayers, reinforcing the city’s role as a unifying force. Its influence extends to Islamic education, where scholars from around the world gather in Saudi Arabia to study and teach about the Prophet’s life, Islamic law, and history.
Economically, Makkah plays a significant role, especially during Hajj season. The pilgrimage brings financial benefits to the region and boosts global economies connected to travel, hospitality, and religious tourism.
Common Questions about the Importance of Makkah in Islam
- Why is Makkah considered sacred in Islam?
- Makkah is sacred due to its association with the Kaaba, the Prophet Muhammad, and its mention in the Quran as a blessed place of worship.
- What role does Makkah play in daily Muslim practices?
- Muslims around the world face Makkah during their five daily prayers, symbolizing unity and devotion.
- What are Hajj and Umrah, and why are they important?
- Hajj is a once-in-a-lifetime pilgrimage, while Umrah can be performed anytime. Both signify devotion, repentance, and a chance to reconnect with Allah.
- Why do Muslims consider the Kaaba so important?
- The Kaaba is viewed as Allah’s house on earth, serving as a focal point of Islamic worship and unity.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Makkah in Islam
In conclusion, the importance of Makkah in Islam extends beyond rituals and landmarks. Makkah is a place of unity, faith, and connection with Allah. Its historical and spiritual role binds Muslims together, serving as a reminder of their shared beliefs, heritage, and divine purpose. Whether through Hajj, daily prayers, or the Kaaba itself, Makkah continues to stand as a timeless symbol of devotion, embodying the essence of Islam.
Makkah’s influence on Muslim life is profound, and its legacy as the heart of Islam endures, guiding Muslims spiritually and morally across generations.
 Colors
Colors 
 Support
Support